Categories
- animatronics (12)
- apple (11)
- arduino (179)
- art (41)
- articles (121)
- artificial intelligence (11)
- automation (421)
- avr (205)
- bitcoin (3)
- breadboard (9)
- cameras (57)
- cars (26)
- cell phones (28)
- clothing mods (21)
- console mods (26)
- dangerous (94)
- desktop mods (24)
- embedded (5)
- flying things (54)
- fpga (22)
- gaming creations (108)
- interface (225)
- internet (17)
- laptop mods (6)
- lasers (22)
- linux (7)
- magnetic (3)
- medical (12)
- microcontrollers (51)
- misc projects (152)
- msp (12)
- music (124)
- pic (90)
- projects (23)
- pyroedu (76)
- raspberry pi (26)
- robots (312)
- security (36)
- sensors (307)
- software (200)
- solar (19)
- stamp (9)
- tools (149)
- tutorials (98)
- Uncategorized (45)
- usb (44)
- wireless (256)
Sponsors


Posted September 27, 2011 by Chris
A “fan cart” is a roughly constant-force device used in introductory physics labs. It consists of a fan (usually a model airplane propeller on a brushed DC motor) mounted on top of a low-friction cart. This article gives a quick overview of the design and includes the software used to make the system work. Take a look!

Posted September 26, 2011 by Chris
This little spider (only 6 legs!) uses some sensors and a Stamp (or PIC) to navigate its way about the world. The article describes how it was built and the custom software that accompanies the project. Also, the article is in german so if you’re not a Deutscher/Österreicher/Schweizer be sure to google translate it.

Posted September 19, 2011 by Chris
A DC servo motor is a powerful tool if you know how to design it properly. They offer high torque and high precision, something that steppers can’t always offer. This article dis-assembles a standard inkjet printer to show you how to experiment with building a low cost DIY servo system. They even recommend using my 10-A H-Bridge! The article is a two parter, so don’t miss both pages.

Posted September 8, 2011 by Chris
One of the primary building blocks of a processor is called the ALU (arithmetic logic unit). It allows for quick and easy arithmetic, sometimes in line with DSP. This project gives a quick introduction for how to make an ALU for a calculator using the Altera UP2 platform.

Posted September 7, 2011 by Chris
A Chess Playing Robot? Hell yeah! In a great display of what one engineer can do with some spare time, here is an automated system that will play chess against you and probably even beat you. This type of robot bridges the gap between playing against a computer on your monitor and actually moving chess piece on a board in real life. See the website for documentation and source code.
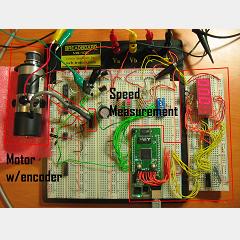
Posted September 6, 2011 by Chris
PWM signals are used all over the place, and for motor control they are a must. Varying the PWM signal will control speed and direction through most motor controllers. This white paper describes one way of making PWM signals with a Xilinx FPGA and also incorporating feedback control from the motor in the FPGA.

Posted September 5, 2011 by Chris
Here’s an article that details out how to access the power system of your car and use it for your own in-car electronics modifications. This project specifically talks about building a DIY security system using a PIC microcontroller and some additional circuitry.

Posted September 4, 2011 by Chris
If you’re an overly obsessive father, this project might be up your alley and making your daughter’s doll house automated might be one step away from trying it on your real house, so why not give it a shot? This article explains how one man mod’d his daughter’s doll house with some automation using a PIC.

Posted August 22, 2011 by Chris
This article demonstrates another way to add some automation to our lives through a device that reminds you when you need to take your medicine. The intelligent part of this project is powered by an arduino / prototino and the rest done through timing and output to an LED that lets you know when the time is up.

Posted August 20, 2011 by Chris
Here’s a CNC panel cutter that uses the NXP mbed platform to give you control to move a drill on x, y and z axis. The platform allows for manual or automatic scripted control of the drill and display output on two 16×2 LCDs. The project documentation is comprehensive as this is a design entry for an NXP contest.






