Categories
- animatronics (12)
- apple (11)
- arduino (179)
- art (41)
- articles (121)
- artificial intelligence (11)
- automation (421)
- avr (205)
- bitcoin (3)
- breadboard (9)
- cameras (57)
- cars (26)
- cell phones (28)
- clothing mods (21)
- console mods (26)
- dangerous (94)
- desktop mods (24)
- embedded (5)
- flying things (54)
- fpga (22)
- gaming creations (108)
- interface (225)
- internet (17)
- laptop mods (6)
- lasers (22)
- linux (7)
- magnetic (3)
- medical (12)
- microcontrollers (51)
- misc projects (152)
- msp (12)
- music (124)
- pic (90)
- projects (23)
- pyroedu (76)
- raspberry pi (26)
- robots (312)
- security (36)
- sensors (307)
- software (200)
- solar (19)
- stamp (9)
- tools (149)
- tutorials (98)
- Uncategorized (45)
- usb (44)
- wireless (256)
Sponsors

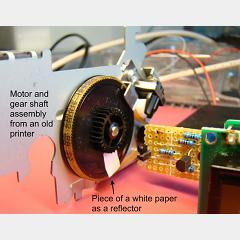
Posted January 17, 2012 by Chris
“The contact with the rotating shaft is avoided with an optical sensing mechanism that uses an infrared (IR) light emitting diode and a photo detecting diode. The IR LED transmits an infrared light towards the rotating disc and the photo detecting diode receives the reflected light beam. This special arrangement of sensors is placed at about an inch away and facing towards the rotating disc.”

Posted January 16, 2012 by Chris
“The idea of building an RS232 to Ethernet bridge seemed like a great way to begin learning about embedded system design. Having created a working sample, though it was left with my teammate after graduation, I decided to recreate the project with more features and higher reliability. The project was later renamed from ‘STEDS’ to ‘NI-1’ (Network Interface 1) and finally ‘Pack-it’. Pack-it is based on a Motorola MC9S12 MCU and a CS8900A Cirrus Ethernet controller.”

Posted January 10, 2012 by Chris
“This was a second-year Embedded Systems Application Project at university. We were given the hardware and after assembling the robot, had to write firmware for it. The PIC MCU programming was done in C. As it was the first time this course was run, objectives were not concrete and were updated as students progressed. Some of the objectives were: follow a line, go over a ramp and memorize a track.”

Posted December 23, 2011 by Chris
“My implementation produces 640×480 signals, but the display is limited to 80×60 blocks…the HCS12 bus can run at 25MHz max, and it takes at least 5 bus cycles to write a byte to an I/O port. For normal VGA, pixels must be written out at a rate of 25MHz.”
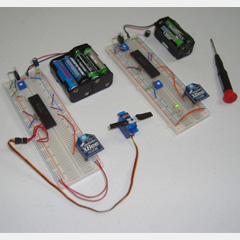
Posted December 22, 2011 by Chris
Today’s article shows you how to build a basic wireless input and output system in the form of a single transmitter and single receiver. Communication is one way to keep things simple with two xbee modules being used for the wireless link. In the end, a small trimpot will control the movement of a servo motor.

Posted December 18, 2011 by Chris
“The robot design allows a single user to easily oversee the operation of a large Kilobot collective, such as programming, powering on, and charging all robots, which would be difficult or impossible to do with many existing robotic systems. The researchers demonstrate the capabilities of the Kilobot as a collective robot, using a 29 robot test collective to implement some popular swarm behaviors.”

Posted December 16, 2011 by Chris
“This project shows how to use a simple thermistor to measure temperature and display the temperature graphically on a Nokia 3310 LCD. Thermistors are incredibly cheap (about 50 cents), and provide fractions of a degree accuracy.”
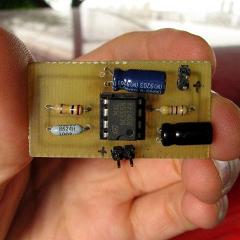
Posted December 14, 2011 by Chris
“This page outlines how to make a simple theft detterant which may be just as effective. The idea is to have a flashing red led indicate that your car is protected. This device can protect your vehicle from potential thieves – it makes it look like your car has an armed alarm system installed, which causes thieves to pass by your car in search of an easier target.”

Posted December 13, 2011 by Chris
“The purpose of this project is to engineer modular software and electronic components, from which it is possible to assemble an intelligent mobile robot suitable for home/office environments. This project aims to fill the gap between the powerful mobile robot platforms typically used by researchers, and the small rug-roving robots with limited processing power that are popular with hobbyists.”
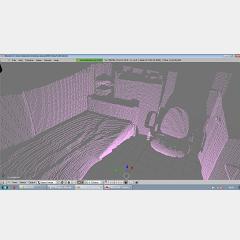
Posted December 10, 2011 by Chris
“How does it work? A digital camera is placed in phonographic rotational axes and records laser light reflections from object’s surfaces (it works better in the dark). Distortion of laser line corresponding to object’s deformations derive the location from the laser source. Constant rotational speed and precise measurment are very important.”







